The Medicare and Medicaid programs are two distinct federal initiatives. Since they are run and funded by different government branches, they primarily assist various constituencies. If you are 65 or older or younger than 65 with a disability, you are eligible for Medicare, a federal program that offers health insurance regardless of your capacity to pay. Those with extremely low incomes may qualify for Medicaid, a joint federal-state health insurance program.
The Distinction Between Medicare and Medicaid
What Exactly Is Medicare?
Medicare is the federal health insurance programme for people aged 65 and up who have limited financial resources and require assistance in needing to pay for medical care and treatment. Seniors and their families can get help paying for medical expenses through this program. There are situations where individuals under 65 with disabilities may qualify for Medicare. Eligibility is determined after carefully reviewing the program's specifics and each instance. Patients with end-stage kidney disease are also eligible for Medicare coverage
Original Medicare
Many retirees in the United States rely on Original Medicare, the government-sponsored health insurance program. Services are provided to hospitalized patients as inpatients (Medicare Part A). Healthcare at home, in a skilled care facility, and even in the hospital are all covered by these plans to varying degrees. Ambulatory care for patients (Medicare Part B). In addition to preventing and diagnosing diseases, these benefits pay for treating existing ones.
Advantages of Medicare
People interested in traditional Medicare benefits but prefer greater flexibility in their coverage options can enroll in Medicare Advantage (Part C). Non-government organizations provide advantage programs for Medicare recipients. These plans fill in the gaps left by Medicare by covering things like prescription drugs, dental, vision, and hearing care.
What Exactly Is Medicaid?
With Medicaid, national and state governments in the United States work together to help low-income families pay for medical care. Major medical procedures and treatments, as well as preventative care, may all factor into these estimates.
How Much Does Medicare Cost Compared To Medicaid?
Medicare Costs
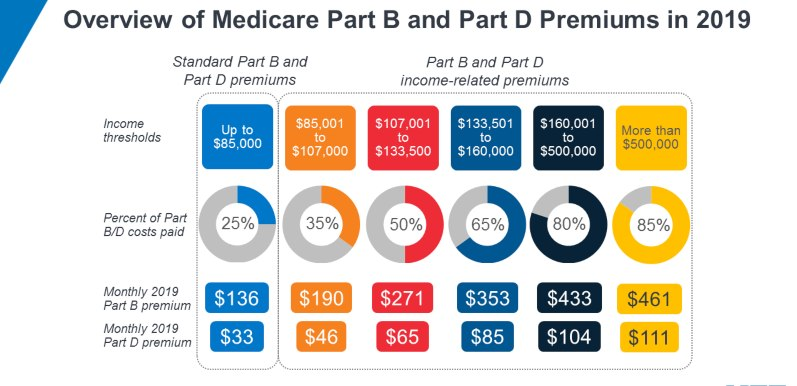
Medicare recipients are responsible for meeting deductibles before their insurance company begins to pay for covered services. Medicare mandates low monthly payments for outpatient services like doctor visits and preventative care but not hospital stays. Prescription medicines, for example, may incur additional out-of-pocket expenses.
Medicaid Costs
Indeed, most Medicaid recipients will not have any out-of-pocket costs when obtaining care, but there are some instances where a nominal copayment will be required. As a type of cost sharing, states are allowed to charge minimal premiums and enrollment fees.
Who Can Get Medicare And Medicaid?
Eligibility for Medicare
The primary criterion for Medicare coverage is a person's age. Applicants must be at least 65 years old and either a citizen or permanent resident of the United States. The number of years of Medicare taxes paid determines premiums and plan eligibility. People under 65 with verified disabilities are an exception to this rule.
Eligibility for Medicaid
Medicaid qualification is generally income-based. It all comes down to household income when determining eligibility.
The Affordable Care Act has established a minimum income criterion that is the same across the country, allowing coverage to be expanded to fill the healthcare gaps for individuals with the lowest incomes. Visit Healthcare.gov to see if you meet your state's financial aid requirements.
Assistance Programs Medicare vs. Medicaid
Medicare Coverage
Various Medicare elements of the program cover a wide range of medical expenses. Medicare Part A pays for a wide variety of in-hospital services, as well as hospice care, certain skilled nursing, and some home healthcare for those who qualify. Outpatient care is covered by Medicare Part B. Outpatient hospital care, doctor's visits, preventative care, and several pieces of medical equipment are all covered under this plan. Medicare Supplement Insurance (Part C)
Medicaid Coverage
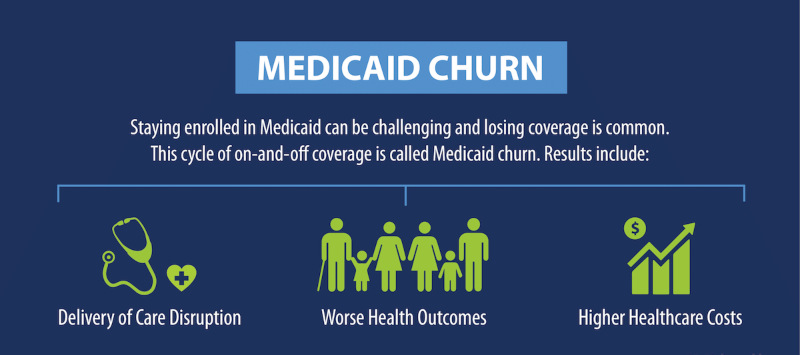
Some benefits are universal to all Medicaid programs, while others are specific to each state's Medicaid system. They consist of the following:
- pediatric checkups and necessary medical care
- Care for Seniors in a Nursing Home
- Adults who need dental surgery
- diagnostic imaging and laboratory tests inpatient and outpatient medical care
- health care options for families, including contraception and maternity care
Conclusion
Medicare and Medicaid are two federally funded health care assistance programs in the United States. These two government-funded programs share a name, and as they both date back to 1965, there is a natural tendency for confusion to arise over their respective functions and scopes of coverage. Those 65 and older or with certain disabilities are eligible for Medicare, which offers medical coverage. Medicare eligibility is unrelated to financial resources.




